PhD/Postdoc/RA (and Visiting Scholar/Prof/Ph.D.) Opportunities in AI, Robotics & Perception at CUHK Hong Kong
[RESEARCH AREA]
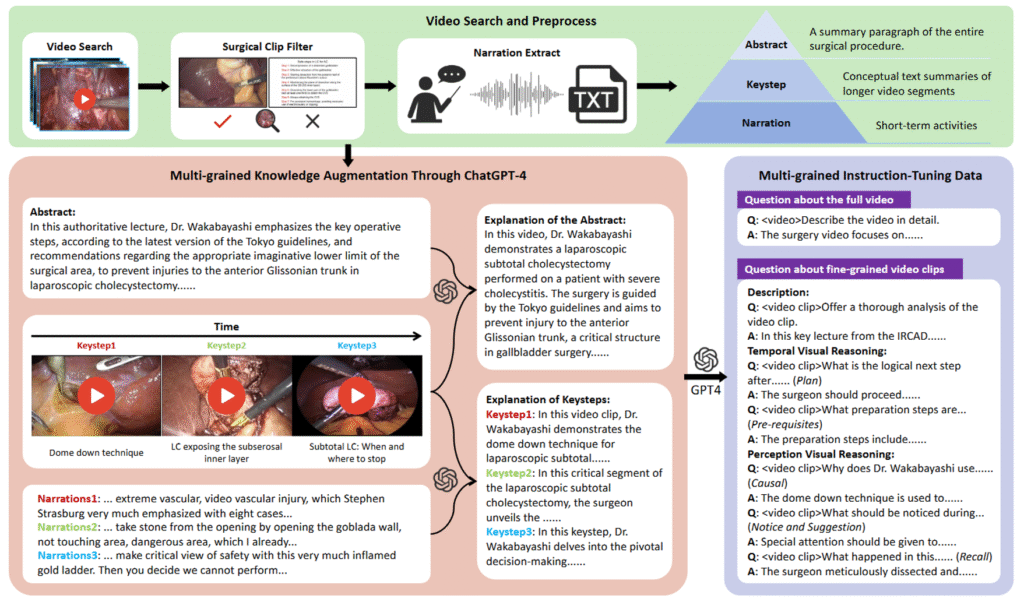
There are multiple openings for Postdoc/RA (and Visiting Scholar/Prof/Ph.D.) to perform research on Medical Robotics Perception & AI at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK, Hong Kong) starting immediately. Particularly, the main areas of interest include AI-assisted endoscopic diagnosis, biorobotics & intelligent systems, multisensory perception, AI learning and control in image-guided procedures, medical mechatronics, continuum, and soft flexible robots and sensors, deployable motion generation, compliance modulation/sensing, cooperative and context-aware flexible/soft sensors/actuators in human environments. For more details, please refer to the recent publications at Google Scholar or the lab website http://labren.org/.
The scholars will have opportunities to work with an interdisciplinary team consisting of clinicians and researchers from robotics, AI & perception, imaging, and medicine.
The salary/remunerations will be highly competitive and commensurate with qualifications and experience (e.g., Postdoc salary will be typically above 4300USD per month plus medical insurance etc.).
[QUALIFICATIONS]
* Background in AI, Computer Science/Engineering, Electronic or Mechanical Engineering, robotics, medical physics, automation, or mechatronics background
* Preferably have hands-on experience in AI/robots/sensors, instrumentation, intelligent systems
* Strong problem-solving, writing, programming, interpersonal, and analytical skills
* Outstanding academic records/publications or recognitions from worldwide top-ranking institutes
* Self-motivated and preferably with strong academic records
[HOW TO APPLY]
Qualified candidates are invited to express their interests through an email with detailed supporting documents (including CV, transcripts, HK visa status, research interests, education background, experiences, GPA, representative publications, demo projects) to Prof. Hongliang Ren ASAP email: <hlren@ee.cuhk.edu.hk> Due to the significant amount of emails, we seek understandings that only shortlisted candidates will be informed/invited to interview.